In the rapidly evolving landscape of technology, one concept stands out for its transformative potential: the Internet of Things, commonly known as IoT. Imagine a world where everyday objects - your coffee maker, thermostat, car, and even your toothbrush - are interconnected, sharing data and working in harmony to make your life easier, more efficient, and more convenient.
This isn't a distant future. it's happening right now.
The Internet of Things refers to the vast network of physical devices around the world that are now connected to the Internet, collecting and sharing data. These "things" can be anything from simple household appliances to complex industrial machines, all equipped with sensors and software to communicate and interact with each other. The fusion of the digital and physical worlds opens up a plethora of possibilities, from smart homes and cities to enhanced healthcare, agriculture, and manufacturing.
In this blog, we'll dive into the fundamental concepts of IoT, explore its diverse applications, and discuss the challenges and opportunities that come with this groundbreaking technology. Whether you're a tech enthusiast, a business leader, or just curious about the buzz surrounding IoT, this guide will provide you with valuable insights into the connected world that's reshaping our future. Join us as we embark on a journey through the fascinating realm of IoT, where the line between the digital and physical worlds blurs, creating new paradigms of interaction and efficiency. Welcome to the Internet of Things - where the future is not just connected, but intelligent.
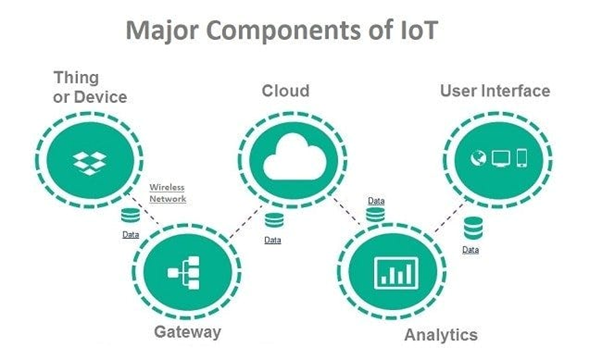
The components leading the list are Sensors and Actuators. Sensors and actuators are at the center of the entire IoT network. Sensors are connected to assets in the form of a physical micro-appliance, embedded into an IoT device. These sensors are responsible for collecting and gathering data to send signals or commands to the actuator. The actuator then responds to the signal or command and "acts" or makes something happen based on this signal. As an example, your office may make use of a smart air conditioning system that is set to a specific temperature. Sensors are used to monitor any changes in temperature in the office environment. If a change is detected, they send a signal to the actuators, which will then automatically adjust the airflow.
Followed by Connectivity. This is largely referred to as the network layer and talks about how data is transferred and processed to ensure seamless communication between connected devices, sensors, the cloud, and actuators. For this to work efficiently, these elements need to be interconnected to understand the data and respond with the appropriate action. This is where IoT protocols and IoT gateways come in. IoT protocols provide a medium of transport for data collected from sensors. Data then goes through an IoT gateway that collects and translates the data being received via the protocols.
IoT Cloud - once the data has traveled through the IoT protocols and gateway, it moves to the cloud. The cloud is a high-performance computing and storage ecosystem that is used for processing and data storage and brings all the different components of IoT together. In the cloud, data is filtered, managed, and stored. The data is then used to provide real-time analytics for fast decision-making about what action should be taken in response to the data collected and signals received.
IoT analytics and data management - this is used to make sense of the large amounts of data being processed. IoT technology can compute all raw data, being collected and transported, into data analytics which provides actionable insights and real-time solutions that can be used for effective decision-making.
Devices and interface - this is the visible component that an IoT user can use to control the system and set their preferences. This interaction is usually conducted on the device itself or remotely via smartphones, tablets, and laptops.
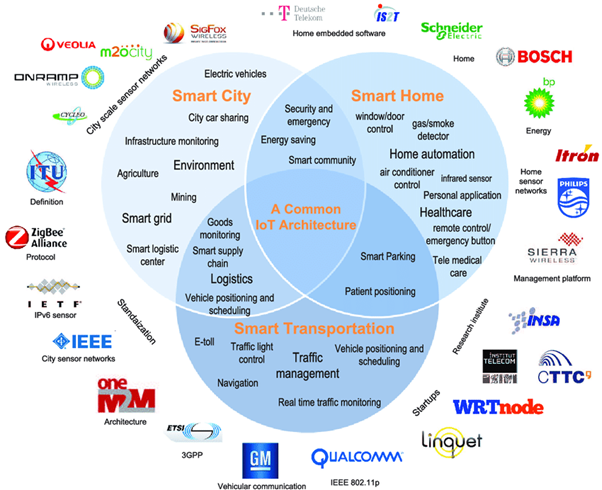
The Internet of Things (IoT) ecosystem is a diverse and multifaceted landscape, comprising a wide range of stakeholders, from hardware manufacturers to service providers and software developers. Here are some key players in the IoT industry ecosystem :
These companies produce the physical hardware components of IoT devices, including sensors, actuators, and embedded systems.
These companies offer the infrastructure and technologies that enable IoT devices to connect to the internet and communicate with each other.
These companies provide the software platforms that facilitate the management, integration, and analysis of IoT data.
These companies and individuals develop applications that utilize IoT data to provide specific functionalities and services, often tailored to particular industries or use cases.
These groups develop and promote standards and protocols to ensure interoperability and security across the IoT ecosystem.
As IoT continues to evolve, collaboration and innovation among these key players will drive the creation of smarter, more efficient solutions that enhance our daily lives and revolutionize industries. Understanding the various components and actors within the IoT ecosystem is essential for leveraging its full potential.
The journey towards a fully connected future is ongoing, and with each step forward, we move closer to realizing the immense possibilities that the Internet of Things holds.